Discussion with Paul Brennan from RCR Reality Check Radio NZ on the next advancement of Australia's (mandatory) Digital ID- TEx as announced by Bill Shorten last week.
A more thorough analysis of Bill Shorten's TEx announcement can be found here:
Australia's mandatory Digital ID is one step closer
It's just a "...digital thumbs up from the government that you are who you say you are."
AUG 18, 2024
On the 12th of August 2024 Bill Shorten, the Australian Federal Minister for Government Services, announced in a press conference the unrolling of the Digital Identity Trust Exchange or TEx for short, which is the infrastructure for the people’s everyday use of Australia’s Digital ID.
Bill spent around an hour spouting weasel words, buzz words and spin. He was vague on concrete details, repeating the words “Consent, Choice, Trust” numerous times. And .. clangers such as:
“All that’s being exchanged is a digital thumbs up from the government that you are who you say you are.” WEASEL WORDS:
My video
This video is in three parts. The first covers shorts from Shorten’s press conference with intercepts of my commentary. The second covers ID2020 the global digital organisation which tasked themselves with creating the global digital ID framework. ID2020 is funded by the likes of Rockefeller, Gavi, Microsoft, and many more powerful corporate entities. I specifically hone in on the 2016 ID2020 press conference at the United Nations sponsored by the UN Office for Partnerships.
This press conference takes an interesting when a journalist from the Inner City Press asks about corruption charges involving the Office For Partnerships. I have a little bit more of a look in to this. After all, if a global Digital ID system is being unleashed on the citizens of the world, coreographed through private interests and the United Nations the people who are going to be under the ID need to feel comfortable with any implications to our life and capacity for autonomy.
I finish with a video I put together about a year ago which show the scope of the Digital ID, the scope the government should be transparent about, but is not.
Bill Shorten’s full address can be found here.
Digital ID Act 2024
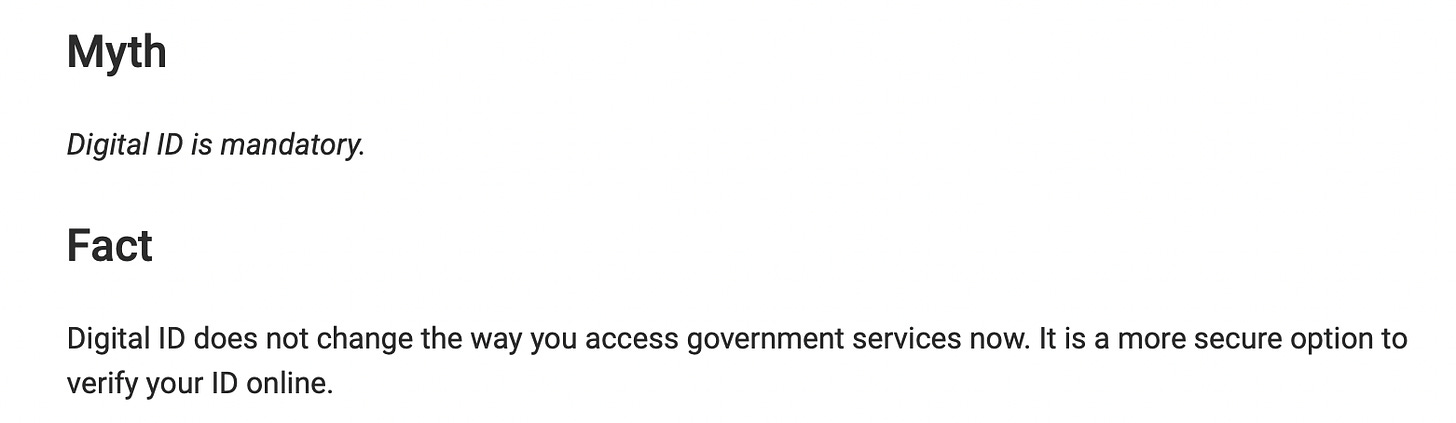
Australia’s Digital ID Bill was passed in May 2024, a mere 3 months ago. A vast amount of people do not want to the Digital ID and the government went to great lengths to assure the public that it was voluntary. Not surprisingly, whilst the Digital ID Act states that Digital ID must be voluntary there are 3 clauses which allow it to be mandatory:
Note the phrase: “Digital ID does not change the way you access government services NOW.’
These clauses allow all businesses to implement a mandatory Digital ID. Though the Act states a Commonwealth company can not enact a mandatory Digital ID, my bet is this will be waived through some extraordinary measure due to a manufactured “crisis” in the years to come.
What does Bill Shorten say vs what is actually said
Australia will “..become the world leader in government service delivery and how we use technology to achieve that goal.”
“Services Australia intersects with every Australian at some point in their lives.” There will be no way around getting a Digital ID.
“Pass keys are a good example of agency innovation that’s made Australia a global pioneer in improving security of online services” Biometrics to be implemented in Digital ID.
“As they say the future is Digital.” As made abundantly clear the future of access to goods and services is online.
“Need to reduce the data used and shared by increasing use of Digital ID” A blatant lie- much more data will collected and stored on people under a Digital ID.
“5.6 million people now use (ing) the My Gov App. But at the moment its potential is under-utilised. Australians, we have a Ferrari in the garage but we only take it out to do the grocery shopping. I want to change that.” Ferrari Bill? How much more clearer can you be that you are out of touch with the average Australian, who is struggling to keep a roof over their head! Bill wants to push more people on to the My Gov App.
“My Gov is the gateway to Australia’s digital future.” You will need a Digital ID to stay current.
Bill unveils TEx: “TEx (Digital Identity Trust Exchange) will not duplicate Digital ID but builds on investments already made in that system. TEx will use My Gov and My Gov ID to make the sharing of personal information more secure and trustworthy. The difference between My Gov and My Gov ID is simply My Gov ID owned by the ATO (Australian Tax Office) is just one thing that proves the identity of government and business. On the other hand, My Gov, owned by Services Australia is a place where you can use your My Gov ID to conduct up 16 Federal government services, and we will add more.” CLEAR AS MUD BILL!
“The strength of this tech trifecta has the potential to give Australian’s control of their data..” WEASEL WORDS!
“We’re opting for the CARROT over the STICK..” Bill is letting us know that if we don’t agree at the carrot stage the stick will be used later.
TEx is a “secure means by which to exchange with a third party who you are, your identity. And what you can do, your credentials.” To show prospective employers your credentials you will need a Digital ID. To access goods and services you will need a Digital ID.
Time frame- By December “TEx will establish the ability to issue a verified credential, ability to selectively share information, and ability to prove your identity without sharing your information… By Jan 2025 the proof of concept will be complete and we will assess what our options are for pilots.”
Here’s how it will work according to Bill- he’s using the My Gov wallet to illustrate:
1. You book a hotel room
Upon booking in the hotel requests your identification (in past drivers license, for e.g.).
With TEx, instead of handing over documents, you scan a QR code on the front desk, like Tap To Pay that digitally shakes hands with your My Gov Wallet.
Secure, blah, blah, blah, decentralised, privacy, blah, blah, blah.
Record in My Gov wallet of how you shared information.
Isn’t that incredible, the government is spending millions upon millions of dollars to streamline our hotel check ins. Wouldn’t have anything to do with the government having real time data on where we are, what we are doing, what goods and services we are accessing? Of course not!
“Choice! Consent! Trust! Choice- you choose what information is shared and with whom. Consent- you deliberately consent to every bit of information that you share. Trust- Information shared is trusted because the system imposes rigorous privacy and security standards to validate its authenticity.” WEASEL WORDS- “Coercion! Obligation! Control! In the future we will not have the choice to not use a Digital ID. You will be coerced into using one for access to goods and services. You will then be centrally surveilled and controlled.
“Alll that’s being exchanged is a digital thumbs up from the government that you are who you say you are.” This is a fundamental shift in government control. The government, in future, will have the power to allow or disallow you access to services in arenas they previously had no control over.
Partnerships
Bill gives a special shout out to Victor Dominello. This fellow, affectionately remembered as fronting up to the daily government covid floggings (can be summed up by “anti vaxxer-get vaxxed.. or else!”) with Bells Palsy, as well as rolling out Covid19 Digital Vaccine Certificates. Victor was the NSW Minister for Customer Service, since leaving politics he has nestled himself into the Wellbeing Digital Government Transformation space, through setting up Service Gen and working hand in hand with the government.
Bill also mentions Mandala Partners. Mandala lists one Co-founder, Adam Triggs. The other Co-Founder seems to be invisible. I wrote to Mandala a few days back to ask for their name/s. I haven’t heard back as of yet, it must be a complex question.
Overhaul of government services
Bill goes on to say they’re overhauling government services. You’ll be surprised to know, I’m sure, that the role of Smart Government is to collect immense amount of data on its “Smart Citizens.” Yay!
Overhauling of Australia’s Privacy Act
I haven’t yet built up the stamina to decode the proposed changes to Australia’s Privacy Act. Guaranteed it will strip us of privacy rights under the weasel wording “strengthening privacy”. I want to put the overhaul on people’s radar, and hopefully someone with legal skills can have a dig around and let the Australian people know what is intended.
What Bill Shorten doesn’t disclose
Bill doesn’t disclose that Digital ID is a requirement under the 2015 United Nations Paris agreement. Target 16.9: By 2030, provide legal identity for all, including birth registration has morphed into every person (besides those who know how to get around it) in the world having a Digital ID.
Bill Shorten neglects to mention ID2020, who have spent at least 8 years working on the Digital ID landscape. Funders including GAVI, Rockefeller, Microsoft and many more powerful players. ID2020 have a partnership with the United Nations. James Corbett covers ID2020 in Corbett Report Episode 415 – The Global Digital ID Prison
I watched the ID2020 launch at the United Nations. This occurred in 2016 and was sponsored by the UN Office For Partnerships:
Whilst watching I became aware of a scandal afflicting the UN in 2016. A corruption blow up, with high officials in the United Nations receiving bribes to do favours using their positions. One of the high ranking UN officials was John Ashe. John was the President of the UN General Assembly, President of the UNICEF Executive Board, and Permanent Representative to the United Nations in New York of Antigua and Barbuda. Before John was able to testify he dropped a barbell on his throat and killed himself.
The case cast serious concerns about the United Nation’s being infected by corruption.
The Journalist raising the scandal was Matthew Lees from Inner City Press. I was impressed by Matthew’s style, the other “journalists” at the press release were just asking for sound bites to make it easier for them to write up their articles. Matthew was a long standing journalist housed at the United Nations, two years later he was thrown out.
How is this relevant to Digital ID? During the 2016 ID2020 press release at the United Nations, Niall McCann Lead Electoral Advisor for UNDP states he wants:
Dialogue within the “UN Family” and industry that allows them to work together on a set of policy principles and identity management, that is shared universally and will advise member states.
Opportunity for the UN to speak to the technology sector and identify new technologies to help the member states to enhance their identity systems.
Private sector financing of identity management systems for nation states through the medium of the United Nations, so we can all work together on the implementation of SDG16.9.
This raises two questions:
Why is Bill Shorten being intentionally non transparent that private interests in collaboration with the United Nations are masterminding the Digital ID and Bill, on behalf of the Australian government, is only implementing the technologies?
How trustworthy is the United Nations?
After all if a centralised Digital ID is being implemented which will track our every move, purchase, decisions etc and will allow or block our access to goods and services, do you want to know who is at the top- creating and implementing the system? I do.
Resources:
https://www.abc.net.au/news/2024-08-13/federal-parliament-live-blog-august-13/104216900
https://www.smartcompany.com.au/technology/government-trust-exchange-initiative-digital-id/
https://ia801809.us.archive.org/15/items/id-2020_202011/ID2020.pdf
https://webtv.un.org/en/asset/k17/k17peww8gf
https://query.prod.cms.rt.microsoft.com/cms/api/am/binary/RE2DjfY
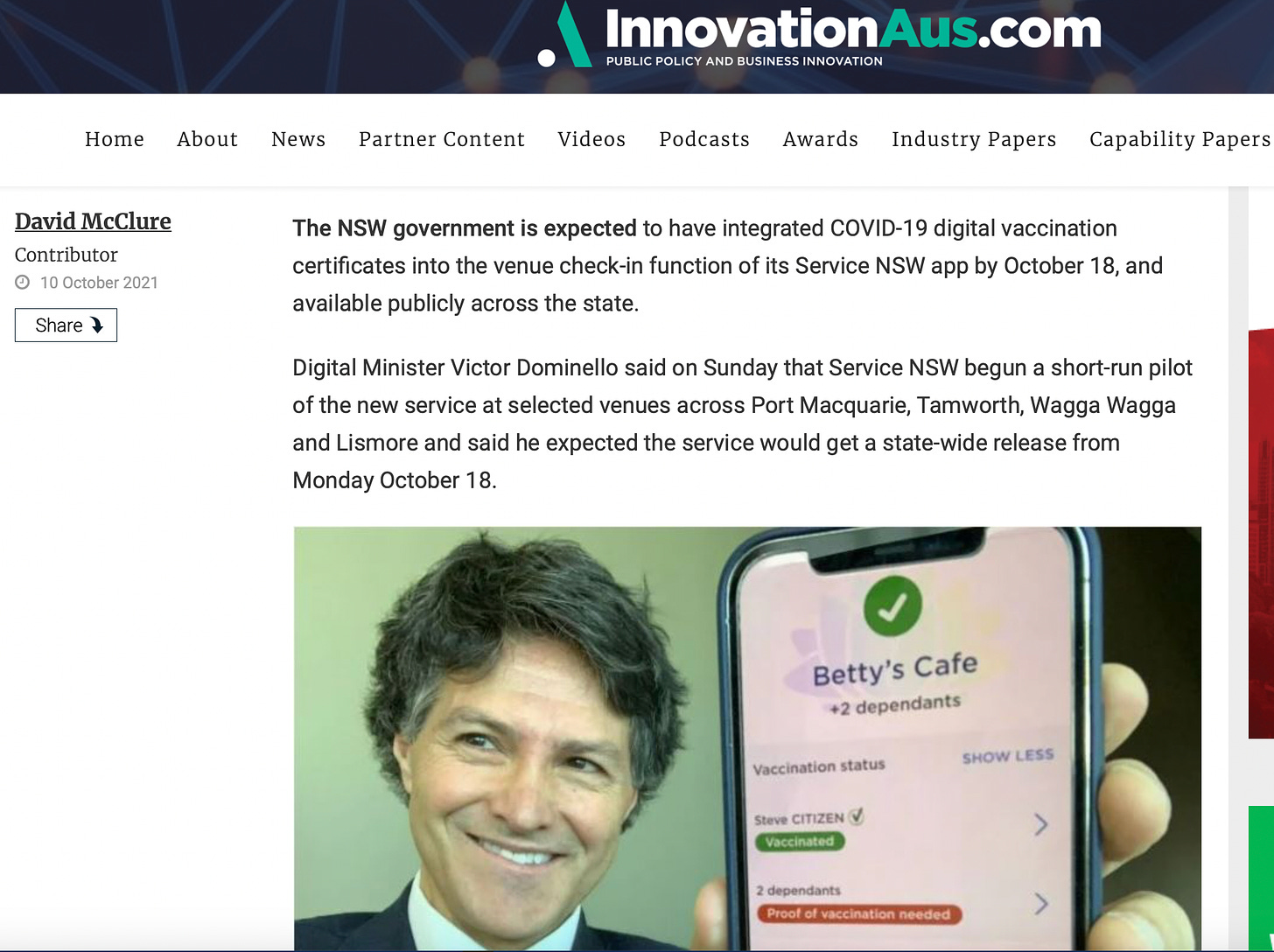
https://www.innovationaus.com/nsw-to-get-digital-venue-vax-passport-from-october-18/
https://www.servicegen.co/our-story
https://www.businessnews.com.au/Person/Damon-Rees
https://www.betterasusual.com/our-team/
https://committees.parliament.uk/writtenevidence/6355/pdf/
https://www.digitalidsystem.gov.au/news/what-australias-digital-id-is-and-isnt
https://www.legislation.gov.au/C2024A00025/asmade/text
https://www.ag.gov.au/sites/default/files/2023-09/government-response-privacy-act-review-report.PDF
https://www.csoonline.com/article/573081/what-is-decentralized-identity.html
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9961047/
https://id4d.worldbank.org
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/09/my-carbon-an-approach-for-inclusive-and-sustainable-cities/
https://webtv.un.org/en/asset/k17/k17peww8gf
https://www.newstatesman.com/world/2013/10/meet-matthew-lee-scourge-united-nations
https://www.cjr.org/the_profile/reporter-expelled-un.php
https://medium.com/id2020/2017-id2020-summit-highlights-and-key-takeaways-95a70c1069f7
Digital IDs are Upon Us
Post 111 (Digital Enslavement Series)
AUG 23, 2024
"Those who desire to give up freedom in order to gain security will not have either one.” — Banjamin Franklin
BLUF: Are digital IDs a benign and inevitable advancement in technology, simply designed to enhace consumer experience or is it part of a greater global conspiracy to strip freedoms and control populations?
Introduction:
Digital IDs are increasingly being positioned as a key component in a broader agenda of enhanced control and surveillance. Initially rolled out in China several years ago, these digital identification systems have been closely tied to the country’s social credit scoring system, which monitors and influences citizens' behavior based on various criteria. This system has sparked global discussions about the potential for digital IDs to extend beyond mere identification to become tools for extensive social and financial control.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has also highlighted the role of digital IDs as integral to the future of digital currencies. According to IMF reports, digital IDs are envisioned as a mechanism to integrate with digital currencies and potentially be linked to forms of social credit scores. This connection could facilitate a more comprehensive and centralized approach to managing financial transactions and personal behavior on a global scale.
Recently, digital IDs have been rolling out worldwide, buoyed by substantial backing and funding from many of the same globalist entities that played a prominent role during the Covid-19 pandemic. These initiatives are not merely technological advancements but are increasingly viewed as elements of a broader strategy aimed at enhancing control and monitoring capabilities. As digital IDs become more widespread, they represent a significant step in the evolution of surveillance and governance, raising important questions about privacy, autonomy, and the implications for individual freedoms.
This essay will explore how China has implemented digital IDs and tied them to digital currencies and social credit scores, before examining the EU, US, and Australia’s progress in this realm. Finally, it will look at key globalist bodies and players that have promoted digital IDs, before examining the overlap and overarching agendas - if any.
China's Digital Control Matrix:
The Intersection of Digital IDs, Social Credit, and Digital Currencies: In recent years, China has emerged as a formidable example of how digital technologies can be harnessed to create an extensive control matrix. This matrix integrates digital IDs, a social credit system, and digital currencies into a comprehensive framework of surveillance and governance. This system is not just a technological marvel but a carefully orchestrated strategy designed to exercise unprecedented levels of control over the lives of its citizens. The origins of this transformation trace back to influential figures like Henry Kissinger and a complex interplay of Western technology companies that helped build the infrastructure for China’s digital control mechanisms.
[Analyst note: notice how the timing/deadline aligns with the Covid-19 “outbreak.”]
The Genesis of China’s Digital Control Matrix: China’s journey towards a sophisticated digital control matrix began with a strategic vision to become the world’s manufacturing hub. This vision was significantly advanced through the efforts of Henry Kissinger, a prominent globalist, who played a pivotal role in opening up China to international trade and investment. Kissinger’s diplomatic initiatives in the 1970s and 1980s helped integrate China into the global economy, creating a pathway for its economic expansion and technological advancement. This transformation was further supported by Western corporations, including Sun Microsystems, Oracle, Google, and Microsoft, which provided the technological infrastructure necessary for China’s digital surveillance capabilities.
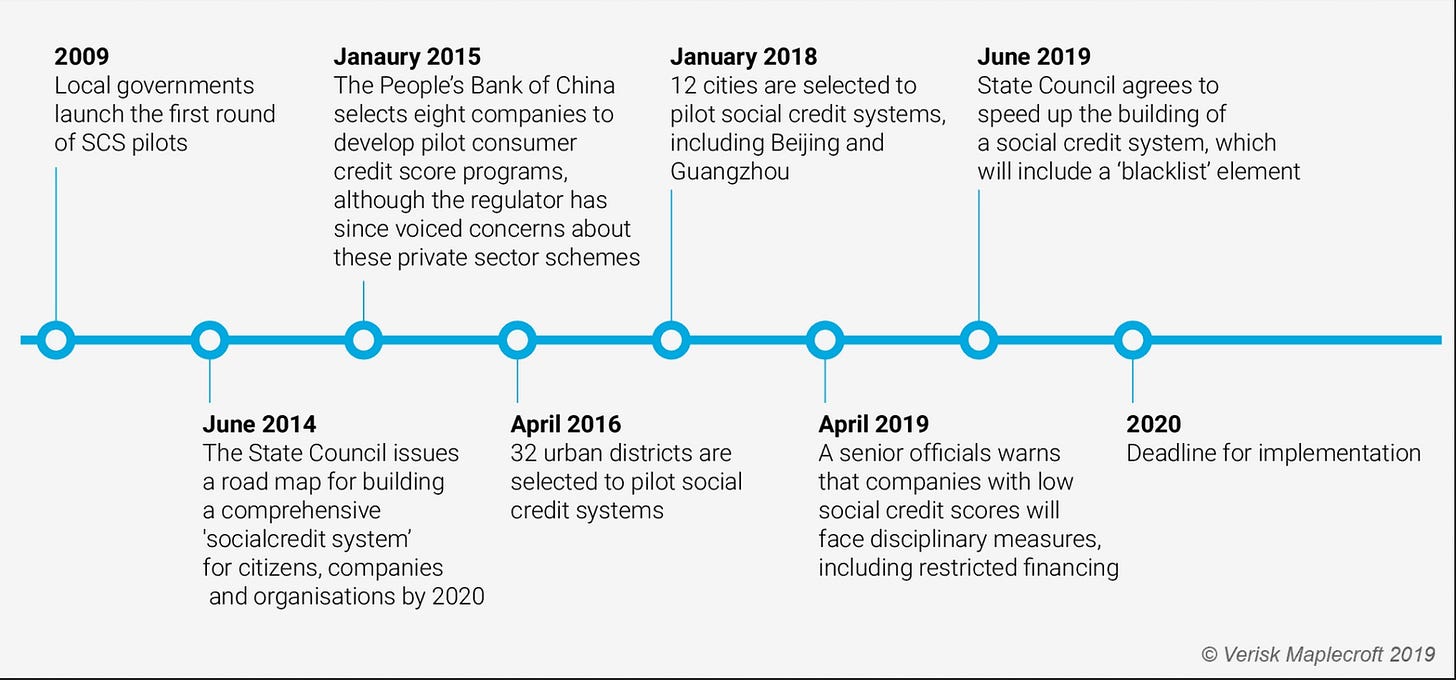
Digital IDs a Timeline: China's push towards digital IDs is a crucial component of its broader strategy to enhance surveillance and control over its population. This initiative has been primarily funded and supported by the Chinese government, with significant contributions from state-owned enterprises and major technology companies such as Tencent and Alibaba. These companies have played a key role in developing the technological infrastructure necessary for implementing digital IDs.
While the drive for digital IDs has largely originated within China, it has received indirect support from global technology companies and institutions. Western corporations like Sun Microsystems, Oracle, Google, and Microsoft have provided critical technological support, which has facilitated China's digital surveillance capabilities. Additionally, international financial institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) have recognized the role of digital IDs in the future of digital currencies, aligning with China's broader digital strategy.
The rollout of digital IDs has followed a defined timeline: initial discussions and pilot programs began in the early 2000s, with a significant push in 2014 to develop a social credit system that integrated digital IDs. By 2016, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology had published a white paper on blockchain technology, laying the groundwork for digital IDs. The proposal for a unified digital ID system was put forth by the Cyberspace Administration of China and the Ministry of Public Security in 2021, with plans for a nationwide system announced in 2022.
Digital IDs in China are intricately linked to the social credit system, which tracks individual behavior and imposes restrictions based on various metrics. These restrictions include real-name registration for internet services, integration with the Digital Currency Electronic Payment (DCEP) system to monitor financial transactions, and limitations on travel and access to services based on social credit scores. This system represents a significant step in the evolution of surveillance and governance, raising crucial questions about privacy, autonomy, and individual freedoms.
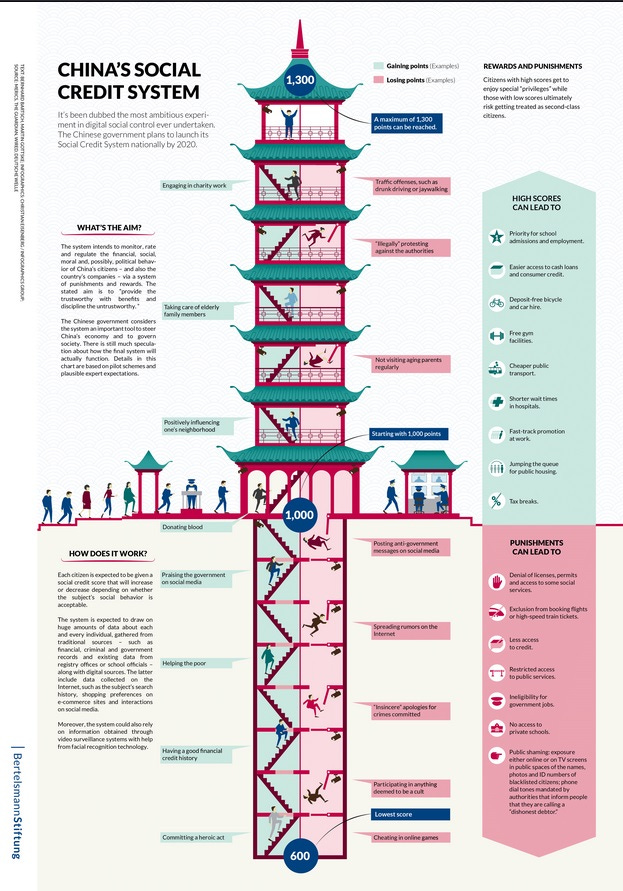
The Digital ID System and Social Credit Score: Central to China’s digital control system is the implementation of digital IDs, which serve as a cornerstone of the nation’s social credit system. This system tracks and assesses individual behavior based on various metrics, ranging from financial transactions to social interactions. The social credit score is a comprehensive measure that influences a person's ability to access services, travel, and even social standing. For instance, a low social credit score can restrict a citizen’s ability to buy plane tickets, access certain public services, or even adopt a pet.
The digital ID system is seamlessly integrated into everyday life in China. From purchasing basic necessities like toilet paper to disposing of trash, digital IDs and facial recognition technology are employed to verify identity and assess eligibility based on social credit scores. These systems rely on advanced AI technologies to ensure that every action is monitored and recorded, reinforcing the overarching control matrix.
The Role of Digital Currencies: Recently, China has introduced its digital currency, the Digital Currency Electronic Payment (DCEP), which is designed to work in tandem with its digital ID and social credit systems. The DCEP aims to create a fully digital monetary system that enhances the government’s ability to monitor and control financial transactions. This digital currency is not just a new payment method but a tool for further integrating financial data with social credit assessments. By tying digital currencies to social credit scores, the Chinese government can exert even greater influence over economic behavior and personal freedom.
Western Technology and China’s Great Firewall: The development of China’s digital control infrastructure was significantly supported by Western technology companies. Sun Microsystems and Oracle contributed to the development of China’s intranet and Great Firewall, systems designed to control and filter internet access within the country. Google and Microsoft provided essential software and technological support, which facilitated the implementation of sophisticated surveillance and censorship mechanisms.
These Western contributions were instrumental in building a digital environment where surveillance and control could be effectively enforced. The Great Firewall, for example, restricts access to international information and ensures that citizens are primarily exposed to state-approved content. This digital barrier is a critical component of China’s control matrix, enabling the government to manage and manipulate information flows and public perception.
Conclusion: The convergence of digital IDs, social credit systems, and digital currencies in China represents a comprehensive approach to governance and control, leveraging advanced technology to monitor and influence nearly every aspect of citizens' lives. The foundation for this control matrix was laid by influential globalists like Henry Kissinger and supported by Western technology companies that contributed to China’s digital infrastructure. As these systems continue to evolve, they offer a glimpse into the potential future of digital governance and control, raising important questions about privacy, autonomy, and the ethical implications of such extensive surveillance. The Chinese model serves as a stark reminder of how technological advancements can be harnessed to create powerful mechanisms of control, shaping the future of global governance and individual freedoms. It also provided the test-bed for these technologies to be thoroughly vetted before their rollout to Western Nations, presently underway.
European Union Drive Toward Digital IDs:
The European Union (EU) has recently intensified its efforts to implement digital IDs, reflecting a broader ambition to modernize its governance and financial systems. This push, however, raises significant questions about privacy and autonomy, as it appears to be following a path similar to the Chinese model of digital control. The integration of digital IDs with digital wallets and potential social credit scores is a key aspect of this evolving framework, mirroring elements of China’s extensive surveillance and control system.
The Evolution and Implementation of Digital IDs in the EU: The drive for digital IDs in the EU has gained momentum in recent years, with legislative actions and policy proposals aimed at creating a unified digital identification system across member states. The EU’s Digital Identity Framework, established by recent laws, is designed to provide a standardized method for verifying identity online and accessing various services. This framework is part of a broader strategy to enhance digital integration and streamline access to public and private sector services.
Key legislative milestones include the “European Digital Identity Regulation” passed in 2021, which mandates the creation of a secure digital ID system that will be recognized across all member states. This regulation aims to “facilitate” easier regulated cross-border transactions, “improve” cybersecurity, and ensure greater convenience for users. The digital ID will integrate with digital wallets, enabling users to store and manage personal information, financial data, and access credentials securely.
Integration with Digital Wallets and Social Credit Scores: One of the most significant aspects of the EU’s digital ID initiative is its integration with digital wallets. The European Commission envisions digital wallets as a way to consolidate various forms of identification, payment methods, and access to services into a single, secure platform. These wallets are sold as a way to enhance convenience but should raise concerns about centralized data management and privacy in end users.
The concept of linking digital IDs to social credit scores has not been explicitly outlined in EU legislation. However, there is growing speculation that the integration of digital IDs with digital wallets could pave the way for systems that monitor and assess individual behavior. In the Chinese model, social credit scores are used to track and influence behavior based on various metrics, such as financial transactions and social interactions. While the EU has not formally adopted a similar social credit system, the potential for future developments in this direction remains a topic of debate.
[Analyst note: it is the contention of this author that Western social credit scores may be similar to modern credit scores, a known entity but with hidden algorithms operating behind the scenes, unbeknown to the majority of people.]
European Vaccination Card will be piloted in five countries (EUVABECO)
‘A European Vaccination Card will enable informed vaccination, according to experts working on the EUVABECO project. Latvia, Greece, Belgium, Germany and Portugal will pilot the new tool from September.’European Vaccination Card will be piloted in five countries - VaccinesToday
The Chinese Model and Its Influence: China’s extensive use of digital IDs and social credit scores provides a reference point for understanding the implications of the EU’s digital ID strategy. In China, digital IDs are closely tied to a social credit system that monitors and controls individual behavior through an intricate network of surveillance and data collection.
The EU’s approach, while officially focused on improving digital convenience and security, bears similarities to the Chinese model in terms of integrating digital IDs with financial and personal data. The drive towards a unified digital identity system, coupled with digital wallets, suggests a gradual move towards a more centralized and comprehensive method of managing and monitoring personal information.
Implications for Privacy and Autonomy: The EU’s push towards digital IDs and digital wallets raises important questions about privacy and individual autonomy. The integration of these technologies has the potential to streamline access to services and enhance security, but it also poses risks related to data protection and government surveillance. As the EU moves forward with its digital ID framework, it will be crucial to address concerns about the balance between technological advancement and the preservation of fundamental rights.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the European Union’s efforts to implement digital IDs and integrate them with digital wallets reflect a significant shift towards a more connected and centralized digital infrastructure. While the EU’s approach is distinct from China’s social credit system, the parallels in digital integration and data management highlight important considerations about privacy and control. As these systems evolve, ongoing scrutiny and debate will be essential to ensure that technological advancements do not come at the expense of individual freedoms and privacy.
United States:
At the federal level, the journey toward digital IDs has been guided by a combination of legislative initiatives, executive orders, and policy frameworks designed to “enhance security” and streamline identity verification processes.
The REAL ID Act of 2005: Although not a digital ID per se, the REAL ID Act set the stage for enhanced identification standards. It mandates that state-issued driver’s licenses and ID cards meet specific security requirements. The Act has prompted states to upgrade their ID systems, laying the groundwork for future digital ID initiatives.
[Analyst note: this is in addition to programs like Nexus, Sentry, Global Entry, TSA-Precheck, etc. Each with an underlying digital component and RFIID technology.]
National Strategy for Trusted Identities in Cyberspace (NSTIC): Launched in 2011 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), NSTIC aimed to promote the development of a framework for secure digital identities. The initiative emphasizes the creation of a secure, privacy-respecting ecosystem where individuals can control their personal information. While NSTIC has not resulted in a single, unified federal digital ID system, it has influenced state and private sector efforts toward digital ID adoption.
Executive Orders and Agency Actions: In recent years, executive orders and actions by federal agencies have furthered the digital ID agenda. For instance, the General Services Administration (GSA) has played a significant role in promoting digital identity solutions for federal employees and contractors. Additionally, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has been involved in developing guidelines and standards to enhance digital identity security.
State Legislation and Initiatives: State-level efforts have been crucial in advancing digital IDs, with various states experimenting with different approaches and technologies.
As of 2024, several U.S. states are actively working on or have implemented digital ID initiatives. Below is an updated list of states with digital ID initiatives, including those with pilot programs, active rollouts, or policies in place:
Arizona
Initiative: Arizona Digital Driver’s License and ID
Progress: Launched in 2021, digital IDs available through a mobile app.
California
Initiative: California Digital Driver's License (DDL) and ID
Progress: Launched in 2021, available through a DMV mobile app.
Colorado
Initiative: Colorado Digital ID
Progress: Launched in 2021, digital ID available via a mobile app.
Indiana
Initiative: Indiana Digital ID
Progress: In development, with initial pilot programs and technology assessments.
Georgia
Initiative: Georgia Digital Driver's License (DDL)
Progress: Pilot program initiated in 2022, with plans for expansion.
Maryland
Initiative: Maryland Mobile Driver’s License (mDL)
Progress: Testing phase since 2022, expanding based on pilot feedback.
Michigan
Initiative: Michigan Digital ID
Progress: Exploring digital ID solutions, with some pilot programs in place.
Missouri
Initiative: Missouri Digital ID
Progress: Exploring digital ID technology and pilot programs.
Nevada
Initiative: Nevada Digital ID
Progress: Launched in 2023, available through a state-sponsored app.
New York
Initiative: New York Digital ID
Progress: Actively exploring digital ID solutions, including partnerships with private sector entities.
Ohio
Initiative: Ohio Digital ID
Progress: In initial development and pilot stages.
South Carolina
Initiative: South Carolina Digital ID
Progress: Digital ID development and pilot testing are underway.
Tennessee
Initiative: Tennessee Digital Driver's License (DDL)
Progress: Early stages of rollout, with ongoing pilot testing and development.
Utah
Initiative: Utah Digital ID
Progress: In development with pilot programs and early implementations.
Washington
Initiative: Washington Digital Driver's License (DDL)
Progress: Pilot testing and initial rollout underway.
The Role of Rockefeller Center in Accelerating Digital ID Adoption:
The Rockefeller Center, a symbol of corporate influence and philanthropy, has played a notable role in shaping and accelerating the adoption of digital IDs in the United States. Its influence significantly impacted federal and state policies, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic when attention was heavily focused elsewhere.
Funding and Strategic Planning: The Rockefeller Center, through its associated foundations and networks, has been instrumental in providing financial support and strategic guidance for digital ID initiatives. During the COVID-19 pandemic, when governments and organizations were urgently seeking solutions for remote operations and enhanced draconian public health measures, the Rockefeller Center’s funding became a critical resource. The emphasis on digital transformation gained momentum as the pandemic highlighted “the need” for more efficient and secure identity management systems.
Rockefeller-affiliated entities have supported research, development, and pilot projects related to digital IDs. Their financial backing helped accelerate the deployment of digital technologies, ensuring that states and federal agencies had the resources needed to explore and implement these systems swiftly. This support included funding for technological infrastructure, policy development, and public-private partnerships aimed at advancing digital ID systems.
Policy Recommendations and Influence: In addition to funding, the Rockefeller Center has played a significant role in shaping policy recommendations related to digital IDs. Leveraging its extensive network and influence, the Rockefeller Center has advocated for the adoption of digital identity frameworks that align with both security and efficiency objectives. Their involvement has included:
Policy Development: The Rockefeller Center’s think tanks and advisory groups have developed policy recommendations that outline best practices for digital ID implementation. These recommendations have been influential in guiding both federal and state governments in crafting regulations and standards for digital IDs.
Strategic Partnerships: By fostering partnerships between technology firms, government agencies, and academic institutions, the Rockefeller Center has facilitated collaborative efforts to advance digital ID technologies. These partnerships have helped bridge gaps between different stakeholders, ensuring a more coordinated approach to digital identity management.
Public Advocacy: The Rockefeller Center has been involved in public advocacy campaigns to promote the benefits of digital IDs. By framing digital IDs as essential for modernizing public services and improving security, they have helped generate support and urgency among policymakers and the general public.
Accelerated Push During the Pandemic: The COVID-19 pandemic provided a unique opportunity for accelerated digital transformation, including the push toward digital IDs. During the lockdowns, as much of the population was preoccupied with immediate health concerns and remote work adjustments, the Rockefeller Center's influence became more pronounced. The distraction caused by the pandemic created an environment where digital initiatives could advance with relatively less public scrutiny.
Governments and organizations, under the pressure to adapt quickly to new challenges, found digital IDs a compelling solution for managing identity verification in a remote and increasingly digital world. The Rockefeller Center’s support during this period was crucial in pushing these initiatives forward, providing both the financial and strategic impetus needed to fast-track digital ID adoption.
Conclusion: The advancement of digital IDs has marked a profound shift in how personal information is managed and monitored, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic—a crisis in which the Rockefeller Center played a significant role. This period, characterized by a manufactured pandemic, provided a unique opportunity for the rapid rollout of 5G infrastructure, which serves as the backbone for the Internet of Things (IoT). This technology enhances and accelerates the tracking of citizens through digital IDs, digital wallets, and digital transactions.
The accelerated deployment of 5G and IoT infrastructure during this time aligns closely with broader agendas, including the World Economic Forum's Great Reset and the 50 in 5 initiative, as well as the ID2020 agenda. Promoted by influential figures such as Bill Gates and Klaus Schwab, these agendas advocate for the integration of digital technologies to reshape global systems. The Rockefeller Center's strategic influence and financial backing have been pivotal in advancing these initiatives, facilitating the rapid implementation of technologies that enable more comprehensive and real-time tracking of individuals.
As digital IDs and related technologies become increasingly embedded in daily life, it is crucial to consider the implications for privacy and individual freedom. While these advancements offer efficiency and modernization, they also raise concerns about enhanced surveillance and control.
Australia:
Australia's journey towards adopting digital IDs reflects a commitment to modernizing public services, enhancing security, and improving efficiency. Over the past decade, Australia has developed and implemented a range of digital identity initiatives and policies. This essay provides an overview of Australia's progress in digital ID rollout, including key initiatives, policies, and the advancements made in integrating digital IDs into various aspects of Australian life.
Digital Transformation Agency (DTA) and Digital Identity Framework: Established to lead digital transformation efforts across the government, the Digital Transformation Agency (DTA) has been instrumental in shaping Australia’s digital identity strategy. The DTA’s Digital Identity Framework aims to create a unified system for verifying and managing identities online. The framework focuses on ensuring interoperability, security, and user control, setting the stage for a comprehensive digital identity ecosystem.
myGovID: A cornerstone of Australia’s digital ID strategy is the myGovID platform, launched in 2019. myGovID is a secure digital identity solution that allows Australians to verify their identity online. It provides access to a range of government services, including tax, social services, and health. myGovID uses multi-factor authentication to ensure secure identity verification and is designed to be a robust and user-friendly system.
[Analyst note: this is very similar to the rollout of DIIA (translated to: the state and me) in Ukraine, after the Russia-Ukraine conflict had begun. The timing was interesting, as it received little coverage, as people were preoccupied with war, and the rollout occurred during a period of uncertainty regarding electric infrastructure, aka the grid. Also interesting is how DIIA was also tied into the Covid-19 vaccine passport iniative for Ukraine. Why rollout a digital product when rolling blackouts are a pervasive threat, unless there is an ulterior motive. Perhaps, using the Ukraine as a test bed for technologies even during a period of kinetic uncertainty.123]
Australia Post Digital Identity: Australia Post has also entered the digital ID space with its Digital ID service, launched in 2020. This service offers a digital identity solution that complements the myGovID platform by providing a secure way for individuals to verify their identity for various transactions. Australia Post’s Digital ID focuses on ease of use and accessibility, integrating with numerous private and public sector services.
National Digital Identity Program: The National Digital Identity Program, introduced by the Australian Government, is a strategic initiative aimed at developing a cohesive digital identity system across the country. This program includes collaboration with various stakeholders, including government agencies, businesses, and technology providers, to create a standardized and secure digital identity infrastructure. It emphasizes user privacy, security, and accessibility.
Policies and Regulatory Framework:
Trusted Digital Identity Framework (TDIF): The Trusted Digital Identity Framework (TDIF) is a set of standards and guidelines developed to ensure that digital identity systems meet high security and privacy requirements. The TDIF is a critical component of Australia’s digital identity strategy, guiding the development and implementation of secure and reliable digital ID solutions.
Digital Transformation Strategy: The Australian Government’s Digital Transformation Strategy outlines the vision for enhancing digital services across the public sector. This strategy includes objectives for improving digital identity verification processes and expanding access to online services. It supports the development of digital ID solutions that streamline interactions between citizens and government agencies, promoting efficiency and convenience.
Conclusion: Australia’s advancement in digital IDs aligns closely with the World Economic Forum's vision of transforming society into a fully digital landscape, where individuals are more easily tracked and regulated by the government. The integration of digital IDs into various aspects of daily life facilitates the linkage of all online interactions, transactions, and movements to a single, verifiable identity. This digital framework supports enhanced monitoring and regulation capabilities, extending to digital vaccine passports and other health-related credentials.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Australia implemented some of the strictest quarantine measures, masking requirements, and vaccine mandates. The government's deployment of technologies such as the home-quarantine app, which used facial recognition and geolocation services, exemplifies this trend. Individuals were required to respond to government verification requests within five minutes, with non-compliance leading to police intervention. Such measures underscore the growing capacity for real-time surveillance and enforcement in a digital society.
As Australia continues to advance its digital identity systems, these developments reflect broader global goals of creating a more controlled and monitored environment. While these technologies offer benefits in terms of efficiency and security, they also raise significant questions about privacy, autonomy, and the extent of governmental oversight.
World Coin:
Worldcoin, a project launched in 2021, is a digital currency initiative co-founded by Sam Altman, along with Max Novendstern and Alex Blania. Its primary aim is to create a global digital currency accessible to everyone, regardless of geographical location or financial status. The project's vision is rooted in the belief that a universally accessible and decentralized digital currency can foster economic inclusion and financial equality.
The core innovation of Worldcoin lies in its use of biometric identification. To participate, users must undergo a biometric verification process using a device called the "Orb," which scans their irises. This process is designed to ensure that each individual can only create one account, preventing fraud and ensuring a fair distribution of the currency.
Founder and Intent: Sam Altman, a prominent entrepreneur and former president of Y Combinator, is the most well-known of the Worldcoin founders. Altman’s career has been marked by a strong focus on technology and innovation. He is also known for his role as CEO of OpenAI, the organization behind ChatGPT.
Exclusive: Altman says ChatGPT will have to evolve in “uncomfortable” ways (Axios)
Altman believes future AI products will need to allow "quite a lot of individual customization" and "that's going to make a lot of people uncomfortable," because AI will give different answers for different users, bas…Worldcoin’s intent is to democratize access to digital currency and to provide a universal basic income (UBI) through its distribution model. The idea is that by giving away a significant portion of Worldcoin to people around the globe, it could address economic disparities and help foster financial inclusion. This ambition reflects a broader trend in the tech industry to leverage new technologies to tackle global issues.
Controversies: Worldcoin has been a subject of controversy from its inception. One of the primary concerns is related to privacy and data security. The biometric data collection required for participation has raised alarms among privacy advocates. Critics argue that storing sensitive biometric information could lead to potential misuse or breaches, despite assurances from the founders about the security measures in place.
Ties to the Occult and Globalist Conspiracy Theories: Sam Altman ties to occult practices has been obfuscated and removed from the Internet. Complaints by prior co-workers for his requested rituals have been removed from the Internet. His marriage to his partner in San Francisco was ritualistic as well.
In the context of globalist theories, Worldcoin and related technologies like digital IDs and digital wallets are sometimes linked to broader narratives about managing and controlling populations. Proponents of these theories argue that digital currencies and biometric identification could be used by powerful entities to exert unprecedented control over individuals’ lives. They suggest that by integrating these technologies into everyday transactions and identity verification, authorities could monitor and influence personal behaviors on a global scale.
Digital IDs, Wallets, and Currencies: Worldcoin is intrinsically linked to the broader movement towards digital IDs, digital wallets, and cryptocurrencies. Digital IDs are increasingly being used for secure and convenient identity verification. Worldcoin's biometric approach aligns with this trend, aiming to provide a secure method for verifying identity in the digital realm.
Conclusion: Worldcoin, spearheaded by influential figures with connections to globalist agendas, represents a notable push towards aligning with the World Economic Forum (WEF), International Monetary Fund (IMF), and United Nations (UN) goals of establishing a unified global governance system. This initiative, which aims to integrate digital IDs, digital wallets, and digital currencies, is part of a broader movement towards comprehensive tracking and control of populations. Worldcoin's ambitious vision includes enhancing financial inclusion and providing a universal basic income, positioning it as a significant development in digital currencies.
However, the project faces considerable challenges and controversies, especially regarding privacy and the practicality of its goals. While speculative connections to globalist and occultist agendas exist, they lack concrete evidence. What is clear is that Worldcoin’s integration with digital IDs and wallets underscores a broader trend toward the digitalization of financial and identity systems. This development highlights both the transformative potential of digital technologies and the significant concerns surrounding privacy, control, and the extent of governmental and institutional oversight in an increasingly digital world.
[Analyst note: this also aligns with a movement by Amazon, Apple, and Google to implement wireless payment technologies tied to an individual, i.e. a form of digital ID and digital wallet, with a digital payment mechanism.45678]
Palantir:
Palantir Technologies, a leading player in the realm of big data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI), stands out not only for its technological innovations but also for its deep connections with government and intelligence agencies. Founded in 2003, Palantir has developed advanced software solutions designed to analyze and integrate vast amounts of data, providing critical insights for various applications. The company’s ties to the Department of Defense (DoD), the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), and influential figures like Peter Thiel underscore its significant role in shaping the intersection of technology and national security. This essay explores Palantir's connections to AI, its funding sources, its origins linked to the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), and its relationships with intelligence and law enforcement agencies.
Palantir and Artificial Intelligence: Palantir Technologies is renowned for its sophisticated use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to process and analyze data. The company’s flagship products, Palantir Gotham and Palantir Foundry, are designed to integrate data from disparate sources, enabling users to uncover patterns, make predictions, and derive actionable insights. These tools are utilized across various sectors, including national security, healthcare, finance, and more.
Palantir’s AI capabilities are central to its mission of transforming data into actionable intelligence. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and advanced analytics, the company’s software helps organizations manage large volumes of complex data, making it possible to detect anomalies, forecast trends, and enhance decision-making processes. This functionality is particularly valuable in contexts where timely and accurate information is critical, such as in security and intelligence operations.
Funding and Ties to DARPA: Palantir Technologies’ early development and funding were closely tied to the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), a key institution in advancing cutting-edge technologies for national security. DARPA’s involvement in funding Palantir reflects its role in supporting projects that have potential military and intelligence applications. The agency’s investment in Palantir underscores its commitment to fostering technological innovations that enhance data analysis and integration capabilities.
In addition to DARPA, Palantir received funding from the Department of Defense (DoD), which has been a significant source of financial support for the company. The DoD’s interest in Palantir’s technology is rooted in its potential to improve military intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance. The integration of Palantir’s software into defense operations highlights the company’s role in supporting national security objectives through advanced data analytics.
Connections to Peter Thiel: Peter Thiel, a prominent entrepreneur and investor, is one of the co-founders of Palantir Technologies. His involvement in the company is notable for its impact on its growth and strategic direction. Thiel’s background in technology and finance, coupled with his influential role in Silicon Valley, has played a significant role in shaping Palantir’s approach to data analytics and AI.
Thiel’s association with Palantir also extends to his broader influence in the technology and investment sectors. As a co-founder of PayPal and an early investor in Facebook, Thiel’s expertise and network have been instrumental in Palantir’s development and success. His connections with other high-profile technology and financial figures have contributed to Palantir’s positioning as a leading player in the big data and AI markets.
[Analyst note: it is interesting to see the ties between Donald J. Trump’s vice presidential pick, JD Vance and Vance’s extensive ties to Peter Thiel. This begs the question of Trump’s ties to globalist aspirations (as the evidence for globalist ties on the political left is overwhelming), as he is often depicted as rooting out the “deep state.”9]
Ties to Intelligence and Federal Law Enforcement Agencies: Palantir Technologies has established strong relationships with various intelligence and federal law enforcement agencies, including the CIA, FBI, and other agencies involved in national security and criminal investigations. These connections are pivotal to understanding the company’s role in the broader landscape of data analytics and intelligence.
The CIA’s investment in Palantir through its venture capital arm, In-Q-Tel, is a notable example of the company’s ties to intelligence agencies. In-Q-Tel’s mission is to identify and support technologies that have the potential to enhance the CIA’s capabilities. Palantir’s data analytics software aligns with this mission by providing advanced tools for analyzing and interpreting large volumes of data, which is crucial for intelligence operations.
Palantir’s collaboration with federal law enforcement agencies, such as the FBI, further underscores its role in supporting national security and criminal justice efforts. The company’s software has been used in various high-profile investigations, including counter-terrorism and organized crime operations. These collaborations demonstrate Palantir’s impact on enhancing the capabilities of law enforcement agencies in addressing complex and multifaceted challenges.
Conclusion: Palantir Technologies, with its deep connections to influential agencies like the Department of Defense (DoD) and DARPA, and its ties to controversial figures such as Peter Thiel, is emblematic of a broader, troubling trend. These same agencies, which heavily funded the controversial handling of the COVID-19 pandemic, are also deeply involved in Palantir’s development and deployment. This entanglement raises significant concerns about the role of advanced artificial intelligence and big data analytics in promoting globalist agendas and supporting potentially corrupt and politically motivated law enforcement entities.
The heavy use of AI and data analytics by these agencies, coupled with their association with dubious intelligence practices, points to a dystopian future where every individual could be secretly tracked and monitored. The technology developed and funded by these entities is not only designed to uncover hidden crimes but also to identify and suppress potential thought crimes before they can manifest as threats to the state. This scenario reflects a disturbing vision of a society where surveillance and preemptive action replace privacy and personal freedoms, creating a system where individuals are continuously monitored and controlled under the guise of security and public safety.
[Analyst note: The Maven Smart System (MSS) - is akin to Terminator’s SkyNet. It is an AI-enabled tool developed with a $480 million contract awarded to Palantir Technologies, significantly enhances battlefield analysis in the Central Command area of responsibility in the Middle East. Co-founded by Peter Thiel, Palantir’s MSS integrates data from various Intelligence Surveillance & Reconnaissance (ISR) systems to aid in target identification and decision-making, using AI to filter and analyze information in near-real time. The system, alongside the National Geospatial Agency’s Broad Area Search – Targeting (BAS-T), scans and identifies enemy systems, interfacing with Army Mission Command Systems for tasks such as generating fire missions. Strategically, the Pentagon aims to leverage MSS and similar AI tools to advance its Combined Joint All-Domain Command and Control (CJADC2) framework, which connects military platforms, sensors, and data streams across the U.S. and its international partners, ultimately improving decision-making and operational efficiency.1011]
International Initiatives:
The 50 in 5 Initiative:
The 50 in 5 Initiative is an ambitious global project designed to accelerate the transition to a digital, inclusive, and sustainable future. Launched with the goal of achieving significant milestones within a five-year framework, the initiative seeks to drive transformative change across various sectors, including digital identity, financial inclusion, and environmental sustainability. This essay delves into the goals of the 50 in 5 Initiative, explores its founders and backers, examines its progress, and investigates its connections to globalist institutions and governments.
50-in-5 Agenda: Digital Slavery by 2028
Goals: The core objective of the 50 in 5 Initiative is to effectuate a rapid transition towards a digital and inclusive global society. Specifically, the initiative aims to achieve the following goals:
Digital Identity: Implementing digital identity systems in 50 countries within five years to enhance access to services and streamline transactions.
Financial Inclusion: Expanding access to digital financial services and instruments to “underserved” populations, aiming for substantial increases in financial inclusion.
Sustainability: Promoting and supporting sustainability initiatives that align with global environmental goals, including carbon reduction and the use of clean energy technologies.
[Analyst note: notice how closely this aligns with sustainable development goals (SDGs), a United Nations initiative.1213]
Founders and Backers: The 50 in 5 Initiative is supported by a coalition of influential figures, organizations, and institutions. Key founders and backers include:
ID2020 Alliance: An integral partner in the initiative, ID2020 focuses on digital identity solutions and aims to provide everyone with a digital ID. Its support for the 50 in 5 Initiative reflects its commitment to enhancing global digital infrastructure.
Bill Gates: The co-founder of Microsoft and a prominent philanthropist, Gates has been a vocal advocate for digital inclusion and sustainable development. His backing of the initiative underscores his interest in leveraging technology for social good.
Klaus Schwab: The founder of the World Economic Forum (WEF), Schwab’s involvement aligns with the WEF’s broader goals of shaping a more equitable and sustainable global future. The WEF's support lends credibility and global reach to the initiative.
Global Governments: Several national governments have endorsed or participated in the 50 in 5 Initiative, reflecting a broad commitment to its goals. These include countries interested in modernizing their digital infrastructure and promoting financial inclusion.
Ties to Globalist Institutions and Governments: The 50 in 5 Initiative is closely aligned with several globalist institutions and governmental bodies, reflecting its integration into broader agendas:
World Economic Forum (WEF): The WEF, under Klaus Schwab’s leadership, has been a strong supporter of the 50 in 5 Initiative. The WEF’s agenda of shaping a more equitable and sustainable global economy complements the initiative’s goals, facilitating its alignment with global policy frameworks.
International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank: These financial institutions have shown support for digital inclusion and sustainability projects, aligning with the objectives of the 50 in 5 Initiative. Their involvement provides financial and strategic backing, enhancing the initiative’s global reach.
United Nations (UN): The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) intersect with the goals of the 50 in 5 Initiative, particularly in areas of financial inclusion and sustainability. The UN’s endorsement of the initiative aligns it with international development agendas.
National Governments: Various governments have endorsed the initiative, reflecting its alignment with national strategies for digital transformation and sustainable development. This support highlights the initiative’s integration into global and national policy frameworks.
ID2020:
The ID2020 Initiative is a pioneering global project aimed at addressing the challenge of digital identity through the development and implementation of secure and inclusive digital identity systems. Launched with a vision to provide every individual with a verifiable digital identity, ID2020 represents a significant step towards modernizing identity management and enhancing access to essential services worldwide. This essay explores the goals of the ID2020 Initiative, its founders and backers, its progress, and its connections to globalist institutions and governments.
Goals of the ID2020 Initiative: The primary objective of the ID2020 Initiative is to ensure that everyone has access to a digital identity that is secure, verifiable, and universally recognized. Key goals include:
Universal Digital Identity: Providing a digital identity to the more than one billion people who currently lack formal identification, thereby improving access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and financial services.
Privacy and Security: Developing digital identity solutions that prioritize privacy and security, ensuring that individuals have control over their personal information and that their data is protected from misuse.
Inclusivity: Creating inclusive digital identity systems that are accessible to all, including marginalized and underserved populations, to bridge the gap between those with and without formal identification.
Interoperability: Ensuring that digital identities can be used across different platforms and services, both nationally and internationally, to streamline interactions and reduce barriers.
Founders and Backers: The ID2020 Initiative was founded with the collaboration of several key organizations and individuals dedicated to advancing digital identity solutions:
Founding Organizations: The initiative was established by a coalition of organizations including the Rockefeller Foundation, Microsoft, and Accenture. These organizations bring a wealth of expertise in technology, philanthropy, and consulting to the initiative, contributing to its strategic vision and implementation.
Peter Thiel: As a notable supporter, Peter Thiel’s involvement aligns with his broader interests in technology and innovation. His backing adds significant influence and financial support to the initiative.
Other Supporters: The initiative also benefits from the support of various technology firms, non-profits, and international organizations that contribute to its goals through funding, technology, and expertise.
Progress and Achievements: Since its inception, ID2020 has made notable progress towards its objectives:
Pilot Projects: The initiative has launched several pilot projects in collaboration with governments and non-governmental organizations. These pilots have tested various digital identity solutions in different contexts, providing valuable insights and refining approaches.
Technology Development: ID2020 has been instrumental in advancing the development of digital identity technologies, including biometric systems and blockchain-based solutions, which enhance security and interoperability.
Partnerships and Collaborations: The initiative has formed strategic partnerships with governments, international organizations, and tech companies to expand its reach and impact. These collaborations have facilitated the deployment of digital identity solutions in various regions.
Ties to Globalist Institutions and Governments: ID2020 is closely connected to several globalist institutions and governmental bodies, reflecting its alignment with broader global agendas:
The Rockefeller Foundation: As a major backer, the Rockefeller Foundation’s support for ID2020 aligns with its mission to advance global health and development initiatives. The foundation’s involvement provides credibility and resources to the initiative.
World Economic Forum (WEF): The WEF’s endorsement of ID2020 reflects its commitment to shaping a more inclusive and digital global economy. The initiative’s goals resonate with the WEF’s broader agenda of promoting digital transformation and global governance.
United Nations (UN): The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) intersect with ID2020’s objectives, particularly in the areas of reducing inequality and promoting access to essential services. The UN’s support underscores the initiative’s alignment with international development frameworks.
National Governments: Several governments have engaged with ID2020 to explore and implement digital identity solutions. These collaborations highlight the initiative’s integration into national strategies for digital inclusion and modernization.
Conclusion: The ID2020 Initiative, with its significant backing from influential entities such as the Rockefeller Foundation, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Peter Thiel, and the World Economic Forum (WEF), exemplifies a broader pattern of globalist alignment in contemporary world events. These key groups, all of which were deeply involved in the Covid-19 pandemic response and the promotion of the Great Reset Agenda, are now at the forefront of advancing digital identity systems through ID2020. This pattern is not merely coincidental but reflects a concerted effort to shape global policies and frameworks.
The intersection of these groups with global agendas is striking. They have not only supported the Great Reset, which seeks to radically transform economic and social systems, but they are also actively promoting climate change initiatives, despite their own lifestyles involving private jets, yachts, and other symbols of extreme affluence. This juxtaposition raises questions about the authenticity of their commitment to sustainability and equity.
Moreover, the push for digital IDs by these influential actors aligns with a broader transhumanist agenda, which seeks to integrate advanced technologies into human life on a fundamental level. The drive towards digital identity systems is part of a larger movement to reshape personal and societal structures, potentially leading to increased surveillance and control under the guise of modernization and inclusivity.
As these powerful groups continue to drive transformative changes across various domains, it is crucial to critically examine their motivations and the implications of their initiatives. The convergence of their efforts across pandemics, climate change, and digital identity underscores a complex and interwoven agenda that reflects broader globalist ambitions.
The Goals:
In recent years, international bodies and influential organizations have increasingly championed digital identity systems as part of a broader global agenda. This initiative, backed by prominent figures and institutions such as the Rockefeller Foundation, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Peter Thiel, and the World Economic Forum (WEF), reflects a significant shift towards comprehensive surveillance and control under the guise of modernization and security. Central to this agenda is the integration of digital IDs with digital wallets, currencies, and social credit systems, which raises profound concerns about privacy, autonomy, and freedom.
Secretive White House Surveillance Program Gives Cops Access to Trillions of US Phone Records (Wired)
Secretive White House Surveillance Program Gives Cops Access to Trillions of US Phone Records
Digital IDs and Surveillance:
The core goal of digital identity systems is to create a unified and accessible platform for managing personal information. While this promises increased convenience and streamlined services, it also opens the door to unprecedented levels of surveillance. Digital IDs, when combined with digital wallets and currencies, enable detailed tracking of every financial transaction, purchase, and movement. This capability allows governments and corporations to monitor individuals’ activities with granular precision.
Moreover, the integration of digital IDs with carbon usage matrices reflects an effort to control and influence personal behavior. Systems designed to track carbon footprints can dictate lifestyle choices, from travel and diet to energy consumption. These metrics could be used to enforce compliance with environmental policies, potentially restricting personal freedoms under the pretext of combating climate change.
Social Credit Systems and Thought Control:
The expansion of digital ID frameworks into social credit systems represents a more insidious form of control. Social credit scores, which evaluate individuals based on their behavior and compliance with certain norms, can influence access to services and opportunities. Coupled with digital IDs, these systems create a comprehensive surveillance network that can assess and potentially penalize individuals based on their actions, attitudes, and even political views.
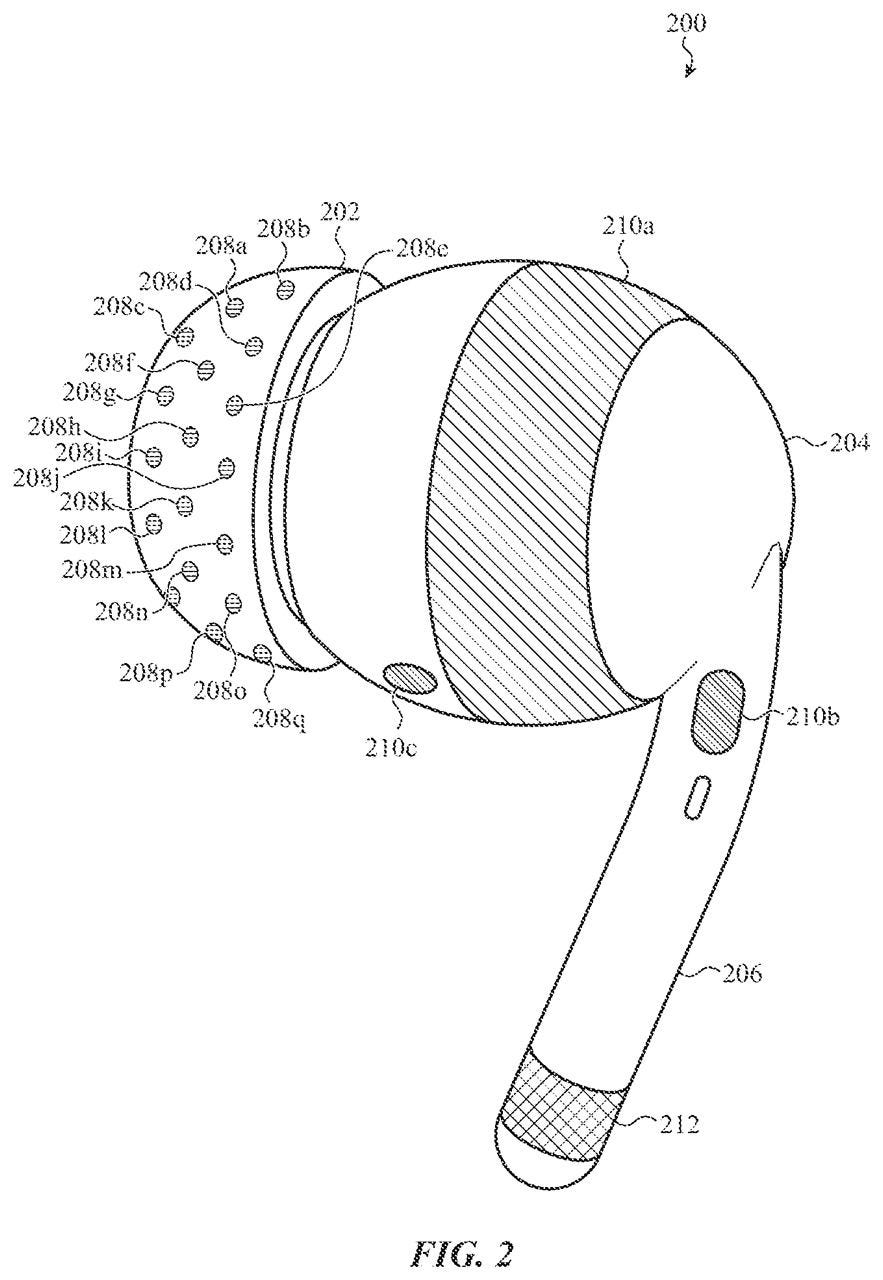
The potential for these systems to monitor and regulate thought is further amplified by emerging technologies. Devices like Apple AirPods and VR headsets, which have patents related to brain activity monitoring, could theoretically contribute to this effort. Although such technologies are still in their infancy, their development suggests a future where even cognitive states could be subject to surveillance and control.
AirPods to Read Your Brainwaves:
Restrictions and Control Mechanisms:
The use of digital IDs and associated technologies facilitates a range of control mechanisms that extend beyond mere surveillance. Governments could implement restrictions on online access and content, limiting information to control public opinion and suppress dissent. Travel restrictions, justified by security concerns or health crises, could be enforced through digital IDs linked to vaccination status and health records. In the wake of pandemics or climate emergencies, these controls could be used to enforce compliance with government mandates.
Dietary restrictions and vaccine requirements could also be tied to digital IDs, as governments and organizations use these systems to track and influence personal health choices. The emphasis on health and safety provides a convenient rationale for implementing such measures, even as they encroach on individual freedoms.
Preemptive Control and Thought Crimes:
A particularly alarming aspect of this agenda is the potential for preemptive control. By integrating digital IDs with social credit systems and surveillance technologies, authorities could act on potential threats before any actual actions are taken. This preemptive approach, akin to the concept of “thought crimes,” enables the removal of individuals deemed problematic based on their behavior or expressed views, thereby stifling dissent and maintaining a controlled environment.
Conclusions:
The pervasive involvement of a select group of powerful organizations and individuals in shaping major global events reveals a troubling pattern of increasing globalist control. From the rollout of digital identity systems through initiatives like ID2020 and the 50 in 5 Initiative to the extensive surveillance and data collection enabled by these technologies, the same influential actors are consistently driving agendas that consolidate power and diminish individual freedoms.
Entities such as the Rockefeller Foundation, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Peter Thiel, and the World Economic Forum (WEF) have played pivotal roles in a series of transformative initiatives—from the management of the COVID-19 pandemic to the promotion of climate change policies and the push for comprehensive digital identity systems. Each of these efforts, while ostensibly aimed at addressing global challenges, aligns with a broader agenda of increasing globalist control.
The integration of digital IDs with digital wallets, social credit scores, and environmental monitoring systems highlights an emerging infrastructure of surveillance and control. This network allows for real-time tracking of individuals' movements, transactions, and behaviors, effectively enabling governments and corporations to exert unprecedented levels of influence. The potential for such systems to monitor cognitive states and enforce compliance through preemptive actions against perceived thought crimes underscores the authoritarian nature of this global push.
The extreme coincidence of these same groups orchestrating significant world events that progressively lead towards greater centralized control suggests a deliberate and coordinated effort to shape a dystopian future. In this envisioned scenario, governments would have the authority to act against individuals based on predictive measures of dissent or non-compliance, removing any potential threats before any actual challenge to the system can manifest. This trajectory towards a one-world government, with its attendant surveillance and control mechanisms, raises profound concerns about privacy, autonomy, and the preservation of democratic values - tied inextricably from the technologies and ideas surrounding 15-Minute Cities.
Paris Olympics 2024 & Planned 15-Minute City - QR Codes, AI, & Drones:
Paris Olympics Will Be a Training Ground for AI-Powered Mass Surveillance
As these globalist agendas continue to unfold, it is essential to remain vigilant about the implications of such centralized control. The convergence of these efforts, driven by a narrow group of influential actors, points to a future where personal freedoms and democratic rights are increasingly at risk. The need for robust safeguards and critical scrutiny has never been more urgent to ensure that technological and policy advancements do not compromise fundamental liberties and human rights.























































uktoo soon